When discussing the features of your soon to be installed Access Control System, you’ll have to decide between fail safe, fail secure, or a hybrid of the two. What is the difference between the two? Simple. Fail Safe means the system is unlocked when power is lost. Fail Secure means the system is locked when the power is lost. As you think about your business, your employees, and all the interior and exterior doors, you’ll want to weigh the Pros and Cons of using fail safe or fail secure. Here is a breakdown of some pros and cons for both formats to ensure you get it right when planning for the installation of your access control system.
Fail Safe
Pros
- Life safety priority: Ideal for exit doors or areas where people must be able to evacuate during a power outage (e.g., stairwells, public buildings).
- Emergency-friendly: Complies with fire codes requiring egress even if power fails.
- No need for key override during outage: Doors automatically open, which helps in evacuation.
Cons
- Security risk during outages: If power is lost, now anyone and everyone can enter your unlocked doors .
- Higher risk of unauthorized access: Less ideal for high-security areas that contain expensive inventory, equipment, or proprietary information.
- Can be manipulated: If attackers disable power intentionally, it opens the door.
Fail Secure
Pros
- Maximum security: Keeps sensitive or restricted areas locked even during outages. Extremely helpful for long-term power outages, like before, during, and after a hurricane.
- Prevents unauthorized entry: Ideal for server rooms, storage, or exterior doors.
- Tamper-resistant: Power disruption doesn’t equal easy access from unwanted intruders.
Cons
- Safety concern during emergencies: May require manual override or backup power to ensure egress.
- Fire code restrictions: Can’t be used in certain exit routes without additional egress options.
- User inconvenience: Without a backup power source, legitimate access may be denied in outages.
Comparison Chart
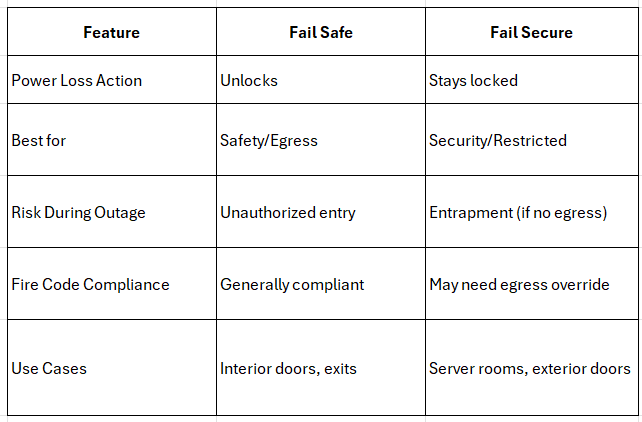
Now that you’ve got the pros and cons, which should you choose for your Charleston-based business? My recommendation is to ensure with both that you have battery backups and failover power supplies when applicable. For fail safe, I see this working best in public buildings and high-traffic areas. For fail secure, it works best when you need to secure your assets and specific secured zones of your building. In the end, be sure to discuss a hybrid system. This can give you the pros of both options to specific doors and areas of business.
